Гост р исо/мэк 20000-1-2013
Содержание:
- Transition from ISO 20000-1:2011 to the 2018 edition
- История
- ITIL Certifications
- Структура стандарта ISO 20000
- Россия и ISO 20022
- Хранилище
- ISO 20000 provides organizations with unlimited growth opportunities
- Certifications and qualification schemes
- New ISO/IEC 20001-1: 2018 will replace its previous edition, which will cease to be valid on 09/30/2021. Transition period started on 09/30/2018
- Parts
- ISO/IEC 20000-1: Service management
- ISO/IEC 20000-2: Guidance on the application of service management systems
- ISO/IEC 20000-3: Guidance on scope definition and applicability of ISO/IEC 20000-1
- ISO/IEC 20000-4: Process assessment model
- ISO/IEC 20000-5: Exemplar implementation plan for ISO/IEC 20000-1
- ISO/IEC 20000-10: Concepts and vocabulary
- References and Links
- Уверенность
- Main differences in ISO 20000:2018
- ¿POR QUE CERTIFICARSE EN ISO 20000?
- ГОСТ Р ИСО/МЭК 20000-1-2013 Информационная технология. Управление услугами. Часть 1. Требования к системе управления услугами
- Применение методологии ISO 20022
- ISO 20000 in brief
- ITIL in practice
Transition from ISO 20000-1:2011 to the 2018 edition
Following the release of ISO 20000:2018, organizations will have to transition their certificates to the latest 2018 edition of the standard. The International Accreditation Forum (IAF) has set the following transition periods and rules:
- 30 September 2018: Organizations may choose to get certified against the 2018 edition from this date. Certifications against the 2011 edition are still acceptable.
- 31 March 2020: All new certifications and re-certifications must be to ISO 20000-1:2018 after this date.
- 29 September 2021: End of the transition period. All existing certificates must be transitioned to ISO 20000-1:2018 before this date. Certificates to the 2011 edition become invalid.
Please note: These transition periods and rules have been set by the International Accreditation Forum (IAF). National accreditation bodies may choose to set slightly different rules — please consult your auditor to find out the precise rules applicable to your organization.
История
Во второй половине 20-го века, в период активного развития электронных расчетов, в Европе и США не было единой государственной расчетной системы, массово доступной для банков, зато существовала и активно развивалась инфраструктура электронных коммуникаций. Как следствие, появилось большое количество частных электронных платежных систем со своими особыми форматами сообщений и бизнес-правилами работы. Банки и корпоративные клиенты этих платежных систем были вынуждены тратить значительные средства на поддержку различных форматов. Неоднократно предпринимавшиеся попытки стандартизации по инициативе «снизу» привели к параллельному существованию значительного количества разных, часто пересекающихся и не всегда согласованных региональных или отраслевых стандартов. Стала очевидной потребность в более глобальном стандарте. В работе над ним активно участвовали представители частных компаний, финансовых институтов и эксперты финансовых рынков, с 2002 года эта работа проводилась в Техническом Комитете 68 «Финансовые операции» (TC 68) Международной организации по стандартизации (ISO, International Organisation for Standardisation). В результате в 2004 году был официально принят стандарт ISO 20022. В настоящее время идет его практическое применение, например, единое европейское платежное пространство (SEPA, Single Europe Payment Area) построено по методологии ISO 20022. Инициатива Федеральной резервной системы (США) по глобальному стандарту для трансграничных платежей IPF (International Payment Framework) также базируется на ISO 20022. География применения ISO 20022 очень широка и включает в себя, например, Японию, Бразилию, Южную Африку. Международные системы, такие как CLS и Euroclear, поддерживают обмен сообщениями, спроектированными в соответствии с ISO 20022, и стимулируют своих участников к переходу на них.
Система межбанковских сообщений SWIFT планирует постепенный переход от применяемых в настоящее время сообщений формата SWIFT MT к сообщениям формата SWIFT MX, которые спроектированы по методологии ISO 20022.
Крупные банки, такие как JP Morgan, HSBC, Deutche Bank и другие, предоставляют своим клиентам по всему миру возможность передавать платежи в формате, спроектированном и размещенном в центральном хранилище ISO 20022.
ITIL Certifications
ITIL certifications offer a tiered approach to learning. Each certification level offers a number of credits to individuals who wish to certify. A certain number of credits must be obtained at each certification level before moving on to the next.
ITIL certifications are for individuals only. Businesses cannot receive ITIL certifications. Each certification level requires a registration fee that ranges in the hundreds, and education can cost thousands of dollars.
Many organizations invest in certifications for their employees. The only drawback of this approach is when a certified employee moves on to another organization the business who paid for the certification has, in some cases, assisted their competition.
Certification Levels arranged by skill level:
- ITIL Foundation
- ITIL Practitioner
- ITIL Intermediate Level
- ITIL Managing Across the Lifecycle
- ITIL Expert Level
- ITIL Master Qualification
Структура стандарта ISO 20000
Международный стандарт состоит из следующих моментов.
1. Менеджмента обслуживания.
2. Учета и распределения средств.
3. Управления ИБ, а также мощностями.
4. Порядка взаимоотношений.
5. Регулирования инцидентов, сложностей, изменений и конфигураций.
6. Проведения аудитов.
Главные процессы, которые в нем происходят, заключаются в следующем:
• предоставление технологии при координации над уровнем и постоянным режимом обслуживания;
• регулирование отношений между поставщиками услуг и клиентами;
• решение и предотвращение сложностей;
• руководство конфигурациями, активами и возникающими изменениями.
Чтобы получить ISO IEC 20000 2011, в компании должны быть интегрированы все процессы. Это поможет в решении многих задач, а именно:
• установить зависимую от реализации процессов связь в самой организации;
• предоставлять необходимые услуги при осуществлении контроля;
• улучшить эффективность процессов;
• обеспечить соответствие IT-технологий потребностям клиентов;
• сделать систему более доступной и надежной;
• измерять качество IT-технологий;
• согласовывать уровень обслуживания.
Россия и ISO 20022
Применение методологии ISO 20022 в России возможно для:
- создания единого стандарта электронных платежей, включающего денежную составляющую расчетов по операциям на фондовом и валютном рынках;
- решения проблем совместимости платежной системы России с международными платежными системами;
- повышения доступности российского финансового рынка для иностранных участников;
- содействия развитию электронного документооборота в смежных отраслях (торговля, отчетность).
Специалистами Банка России проводится работа по анализу развития стандарта ISO 20022 и практики его применения, для чего организовано взаимодействие с Федеральным агентством по метрологии и сертификации, представляющим Россию в ISO, с целью подключения Банка России к работе комитета ТС 68. Проводится обсуждение плана основных мероприятий по созданию национального стандарта безналичных расчетов с использованием схем электронных сообщений, построенных по методологии международного стандарта ISO 20022, в рамках которого запланированы консультации с государственными учреждениями, участниками финансовых рынков и их ассоциациями.
Хранилище
Единое централизованное хранилище (репозитарий) является центром знаний по ISO 20022 и открыто для просмотра с целью исключения различий в использовании одних и тех же элементов и согласования порядка работы.
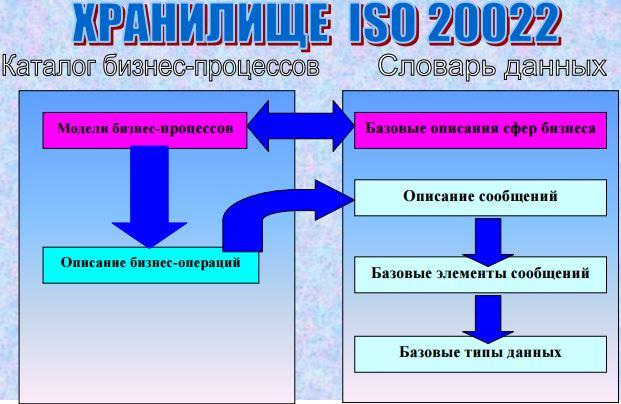
Хранилище логически делится на словарь данных и каталог бизнес-процессов. Словарь данных включает в себя описание базовых сфер бизнеса (например, Forex, операции с акциями), определение сообщений, их базовых элементов (например, электронно-цифровая подпись (ЭЦП) и типов данных (например, код валюты, банковский идентификационный код (BIC – стандарт ISO 9362). Каталог бизнес-процессов содержит модели финансовых бизнес-процессов, описания конкретных бизнес-операций со ссылками на используемые сообщения.
Также в хранилище содержится вся история изменения его данных. Инициативы пополнения хранилища исходят от заинтересованных участников рынка, проходят многоступенчатый процесс одобрения экспертами, выбранными представителями финансовых институтов и ISO, после чего регистрируются и вносятся в хранилище. Таким образом, управление процессом развития стандартов по методологии ISO 20022 близко к саморегулированию.
ISO 20000 provides organizations with unlimited growth opportunities
Adding ISO certifications allow your business to grow in a number of strategic ways.
Firstly, by offering the opportunity to certify your business instead of your employees, ISO 20000 provides you with a boost in reputation and credibility that isn’t reliant on keeping the same employees. If an employee leaves your company for a competitor, you don’t have to worry about them bringing over skills they learned because they worked for you.
Moreover, having an ISO 20000 certification builds customer confidence. It allows your company to compete with an elite group of certified contractors all vying for a piece of the client’s portfolio.
But perhaps the best way ISO 20000 certification allows your business to grow, is by providing a stable foundation of superior service levels that you can build upon as you add services and gain new clients. It’s a fully scalable model that helps businesses of all sizes achieve peak efficiency.
Certifications and qualification schemes
As with most ISO standards, organizations and individuals seek training towards establishing knowledge and excellence in applying the standard. The certification scheme targets organizations, while the qualification scheme targets individuals.
Qualification of individuals is offered by URS, APMG-International, EXIN, PECB, Loyalist Certification Services, TÜV SÜD Akademie, PEOPLECERT, and IRCA.
The EXIN, Loyalist and TÜV SÜD program is in fact a qualification in IT Service Management based on ISO/IEC 20000 and includes a Foundation level and several role based certificates: professionals in Align, Deliver, Control and Support, Associate, (Executive) Consultant/Manager and Auditor.
The APMG qualifications are focused on getting an organization certified and presume knowledge of IT Service Management is already available. The APMG qualifications are conducted at the Foundation, Practitioner and Auditor level.
IRCA and other organizations involved in the certification of auditors have developed their own auditor training and certification for ISO/IEC 20000 auditors.
In terms of certification, there are leading certification bodies around the world, for instance, BSI in UK, Quality Austria in Austria, JQA in Japan, KFQ in Korea and SAI Global in Australia, Asia and Americas.
New ISO/IEC 20001-1: 2018 will replace its previous edition, which will cease to be valid on 09/30/2021. Transition period started on 09/30/2018
Main changes and improvements
The standard has been rewritten to guarantee service management integrated and aligned with different corporate strategies, making services management system performance more effective for organisations, customers and suppliers. The standard adopts the HLS (High Level Structure) structure common to all the new ISOs (e.g.: ISO 9001: 2015, ISO/IEC 27001: 2013) allowing the best interaction of multiple integrated management systems.
Main changes introduced concern:
- incident management, service request management, availability management, service continuity management, service level management, service catalog management, capacity management and demand management have been distinguished;
- the prescriptive sections of the standard have been reduced so as to make the application of the service management systems easier for any organisation;
- the required documentation supporting the service management system have been reduced so as to make its definition more strictly aligned with the organisation needs;
- the design, build and transition process definition for the service has described more precise way.
Certificates can be updated during any audit scheduled before 09/30/2021.
However, the IAF (International Accreditation Forum) decided that all initial and recertification audits must comply with the 2018 version of the standard 18 months after transition starting date. It is important, therefore, to timely plan the implementation of the new requirements and, consequently, the transition audit execution.
Expiry date of the certifications issued in accordance with ISO/IEC 20000-1: 2011 during the transition period will coincide with the end of the transition period itself.
During the transition period, already certified organisations can choose to make the transition to the new standard:
- during a surveillance audit
- during a recertification audit
- in-between to programmed audits, programming an extra audit.
What action should be taken to prepare for the transition to the new standard?
- Familiarise with the standard contents and perform a gap analysis between new requirements and current organisation’s systems procedures;
- Carry out training for interested personnel to prepare them understanding the main changes;
- Plan the implementation of all necessary changes to the service management system;
- Get in contact with the reference person, in order to program the transition and execute the audit;
- Assess the implementation effectiveness through internal audits, and define further actions if necessary.
Parts
ISO/IEC 20000-1: Service management
Formally: ISO/IEC 20000-1:2018 (‘part 1’) specifies requirements for «establishing, implementing, maintaining and continually improving a service management system (SMS). An SMS supports the management of the service lifecycle, including the planning, design, transition, delivery and improvement of services, which meet agreed requirements and deliver value for customers, users and the organization delivering the services.». The 2018 version (ISO/IEC 20000-1:2018) comprises ten sections, following the high-level structure from Annex SL of the Consolidated ISO/IEC Directives, Part 1:
- Scope
- Normative references
- Terms and definitions
- Context of the organization
- Leadership
- Planning
- Support of the Service Management System
- Operation of the Service Management System
- Performance Evaluation
- Improvement
ISO/IEC 20000-2: Guidance on the application of service management systems
ISO/IEC 20000-2:2019 provides guidance on the application of service management systems (SMS) based on the requirements in ISO/IEC 20000-1:2018.
ISO/IEC 20000-3: Guidance on scope definition and applicability of ISO/IEC 20000-1
ISO/IEC 20000-3:2019 provides guidance on scope definition, applicability and demonstration of conformance for service providers aiming to meet the requirements of ISO/IEC 20000-1, or for service providers who are planning service improvements and intending to use ISO/IEC 20000 as a business goal. It supplements the advice in ISO/IEC 20000-2, which provides generic guidelines for implementing an SMS in accordance with ISO/IEC 20000-1.
ISO/IEC 20000-4: Process assessment model
ISO/IEC TR 20000-4:2010 has been withdrawn. A set of new documents providing a Process Reference Model (PRM) and a Process Assessment Model (PAM) based on ISO/IEC 20000-1:2018 is being developed by ISO/IEC JTC1/SC7 in the 33000 series of standards.
ISO/IEC 20000-5: Exemplar implementation plan for ISO/IEC 20000-1
ISO/IEC TR 20000-5:2013 service providers on how to best achieve the requirements of ISO/IEC 20000-1. ISO/IEC 20000-5 will be updated based on the current version of ISO/IEC 20000-1.
ISO/IEC 20000-10: Concepts and vocabulary
ISO/IEC TR 20000-10:2018 describes the core concepts of ISO/IEC 20000, identifying how the different parts support ISO/IEC 20000‑1:2018 as well as the relationships between ISO/IEC 20000 and other International Standards and Technical Reports. This part of ISO/IEC 20000 also explains the terminology used in the ISO/IEC 20000 series, so that organizations and individuals can interpret the concepts correctly.
References and Links
- International Organization for Standardization: ISO/IEC 20000-1:2011, Information technology — Service management — Part 1: Service management system requirements. — Geneva, Switzerland, April 2011.
- International Organization for Standardization: ISO/IEC 20000-1:2018, Information technology — Service management — Part 1: Service management system requirements. — Geneva, Switzerland, September 2018.
Learn more about the ISO20000 standard in the following sections:
- What is ISO 20000?
- FAQ: ISO 20000 certification
- Use cases: How the YaSM model supports your ISO 20000 project
- How YaSM relates to ISO 20000
- The YaSM — ISO 20000 Bridge
Уверенность
нам доверяют
Клиенты
Команда Менделеев Тест эффективно взаимодействует в области проведения испытаний продукции как с производителями только выходящими на рынок, так и с известными компаниями, поставляющими продукцию для различных отраслей промышленности. Мы ценим каждого нашего клиента и гордимся сотрудничеством с крупнейшими производителями и поставщиками общепромышленного оборудования.
ГК «Севкабель», Производственное объединение «ОВЕН» и многие другие клиенты доверяют нам и продолжают плодотворное сотрудничество!
мы доказываем на практике
10-летний опыт
В течение 10 лет мы совершенствовали свои бизнес-процессы, технологическое обеспечение лаборатории и форматы предоставления услуг, чтобы сотрудничество с Менделеев Тест Групп было плодотворным и удобным для наших клиентов.
У нас имеется все необходимое оборудования для проведения испытаний и налажены тесные деловые контакты со многими отечественными и международными испытательными центрами для комплексных испытаний сложного технического оборудования.
Main differences in ISO 20000:2018
The main differences between ISO/IEC 20000:2018, Part 1 and the previous 2011 edition are as follows:
- A new high-level document structure has been introduced in line with other management system standards, making it easier for organizations to comply with several standards such as ISO 9001 (Quality Management) or ISO 27001 (Information Security Management).
- Terms and definitions have been revised to include terms specific to management system standards. A reference has been added to the terms and definitions given in ISO/IEC 20000-10.
- Clauses have been revised or added to take into account the growing trends in service management, such as commoditized services and the management of multiple service providers by a service integrator.
- Some detail has been removed to allow organizations more flexibility in fulfilling the requirements.
- An explicit requirement to «establish, implement, maintain and continually improve a service management system (SMS)» has been introduced.
- References to the «PDCA» («Plan-Do-Check-Act») methodology have been deleted because many improvement methods can be used with management system standards.
- New requirements for context of the organization and actions to address risks and opportunities have been added.
- Requirements for documented information, resources, competence and awareness have been updated.
- Additional requirements for service planning, knowledge, asset management, demand management and service delivery have been inserted.
- Requirements for incident management and service request management have been separated out into two sets of requirements.
¿POR QUE CERTIFICARSE EN ISO 20000?
-
Implantar la norma ISO 20000 ayudara a su su organización a evaluar su Gestion de servicios TI consiguiendo:
- Mejorar sus servicios,
- Demostrar la capacidad de su empresa para cumplir con los requisitos del cliente
- Adquirir una herramienta para la evaluación independiente de la calidad de sus servicios.
- Obtendrá una diferenciación competitiva al demostrar confiabilidad y alta calidad de servicio;
- Facilita el acceso a mercados clave, ya que muchas organizaciones en el sector público y grandes empresas exigen que sus proveedores de servicios de TI demuestren conformidad con ISO 20000;
- Mejora la confianza de sus clientes mediante la seguridad de que se cumplirán sus requisitos de servicio;
- Instaura en su empresa un nivel medible de efectividad y una cultura de mejora continua al permitir a los proveedores de servicios monitorear, medir y revisar sus procesos y servicios de administración de servicios;
- Reduce los costos de conformidad con una multitud de regulaciones como por ejemplo PCI DSS
- Facilita el poder aprovechas las mejores prácticas de ITIL para optimizar recursos y procesos.
Si desea conocer los costes asociados a la implantación de la Norma, en los siguientes enlaces puede obtener la información que necesita:
Obtenga Aquí un de la implantación de la Norma.
Presupuesto Online
Solicite Aquí de la implantación de la Norma.
Contáctanos
ГОСТ Р ИСО/МЭК 20000-1-2013 Информационная технология. Управление услугами. Часть 1. Требования к системе управления услугами
- 35. Информационные технологии. Машины конторские.
- 35.20. Информационные технологии (ит) в целом *включая общие аспекты информационно-технологического оборудования
- Статус документа:
- принят, введён в действие 01.01.2015
- Название на английском языке:
- Information technology. Service management. Part 1. Service management system requirements
- Дата актуализации информации по стандарту:
- 30.11.-0001, в 00:00 (более года назад)
- Вид стандарта:
- временно не известен
- Дата начала действия ГОСТа:
- 2015-01-01
- Число страниц:
- не известно
- Назначение ГОСТ Р ИСО/МЭК 20000-1-2013:
- Данная часть ИСО/МЭК 20000 является стандартом Системы управления услугами (СУУ). Здесь представлены требования к поставщику услуг по планированию, созданию, внедрению, эксплуатации, мониторингу, анализу, поддержке и совершенствованию СУУ. Требования охватывают проектирование, преобразование, предоставление и совершенствование услуг для обеспечения соответствия требованиям к услугам.
Данная часть ИСО/МЭК 20000 может использоваться:
a) организацией, нуждающейся в поставщиках услуг и требующей гарантий обеспечения выполнения соответствующих требований к услугам;
b) организацией, требующей последовательного и согласованного подхода от всех поставщиков услуг, в том числе в цепочке поставок;
c) поставщиком услуг, который намерен продемонстрировать свои способности по проектированию, преобразованию, предоставлению и совершенствованию услуг для обеспечения выполнения соответствующих требований к услугам;
d) поставщиком услуг для мониторинга, измерения и анализа своих процессов управления услугами и услуг;
e) поставщиком услуг для совершенствования проектирования, преобразования и предоставления услуг за счет использования результативного внедрения и эксплуатации СУУ;
f) экспертом или аудитором в качестве критерия для оценки соответствия СУУ поставщика услуг требованиям этой части ИСО/МЭК 20000.
Все требования в данной части ИСО/МЭК 20000 носят общий характер и предназначены для применения ко всем поставщикам услуг независимо от типа, размера и характера предоставляемых услуг
- Ключевые слова документа:
- система управления услугами
Нормативные ссылки из текста ГОСТ Р ИСО/МЭК 20000-1-2013:
- Ссылки на ГОСТы:
- ГОСТ 29285-92
Применение методологии ISO 20022
Конечной целью применения методологии ISO 20022 в той или иной предметной области (например, безналичные расчеты) является обеспечение информационного обмена с помощью сообщений, соответствующих данному стандарту.
Решение указанной задачи зависит от текущего состояния предметной области, с которого начинается переход к применению сообщений ISO 20022, и наличия в Репозитории сообщений, покрывающих потребности информационного обмена в данной предметной области. В рамках ISO 20022 рассматриваются три варианта:
- не существует ни сообщений ISO 20022, соответствующих предметной области, ни устоявшегося перечня сообщений в рамках предметной области;
- в предметной области имеется перечень сообщений, обеспечивающих информационный обмен, но в Репозитории ISO 20022 аналогичные сообщения отсутствуют;
- в предметной области имеется перечень сообщений, обеспечивающих информационный обмен, в Репозитории ISO 20022 также имеются аналогичные сообщения.
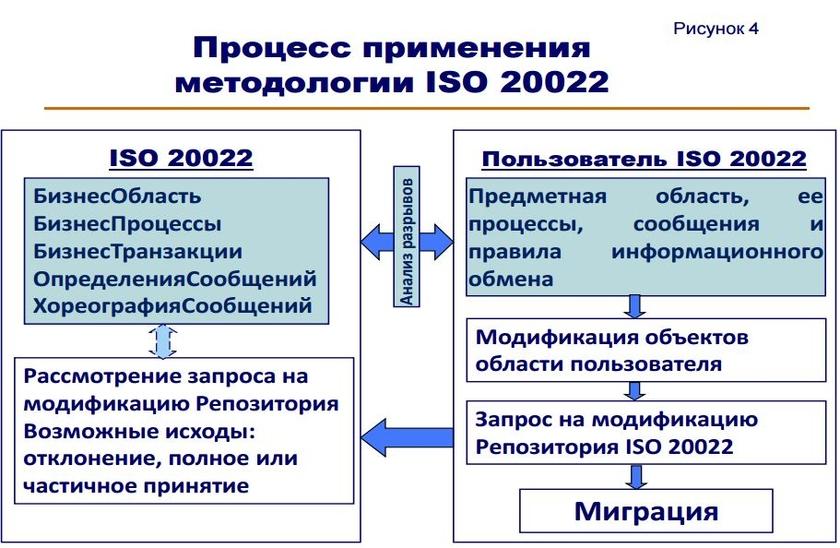
Рекомендации по осуществлению перехода к использованию сообщений ISO 20022 для указанных случаев рассматриваются в рамках единого подхода, называемого «обратное проектирование». Состав мероприятий обратного проектирования укрупненно может быть представлен в виде следующей последовательности этапов.
- Проверка наличия в составе ISO 20022 БизнесОбласти, совпадающей или сходной с предметной областью, для которой планируется применение ISO 20022 (Например: безналичные расчеты и БизнесОбласть ISO 20022 «Платежи»).
- Сопоставление состава и свойств операций в рассматриваемой предметной области с составом и свойствами БизнесПроцессов в соответствующей БизнесОбласти ISO 20022.
- Документирование совпадений и отличий (анализ разрывов в БизнесОбласти).
- Сопоставление состава и свойств сообщений в рассматриваемой предметной области с составом и свойствами МножестваСообщений для соответствующей БизнесОбласти ISO 20022 с последующим документированием (анализ разрывов в ОпределенииСообщений).
- По результатам анализа разрывов: создание новых и/или модифицированных БизнесПроцессов и/или ОпределенийСообщений, соответствующих ISO 20022
- Регистрация в Репозитории ISO 20022 изменений и дополнений в БизнесПроцессах и/или ОпределенияхСообщений11
- Планирование и осуществление миграции к МножествуСообщений ISO 20022.
Ниже на Рисунке 4 приведено схематическое представление данного процесса.
ISO 20000 in brief
ISO/IEC 20000 is the international standard for service management, applicable to all service providers, regardless of type, size and nature of the services delivered.
Part 1 of ISO/IEC 20000 (ISO/IEC 20000-1) specifies requirements for «establishing, implementing, maintaining and continually improving a service management system (SMS)». These are which must be fulfilled by organizations to be compliant with the ISO 20000 standard.
The standard was first published in 2005 and subsequently updated in 2011.
A third, completely revised version of the standard (referred to as ISO/IEC 20000-1:2018) was released on 15 September 2018.
ITIL in practice
Globally, ITIL is the most widely accepted approach to the management of IT services. ITIL’s framework creates an environment of continuous improvement where all of an organization’s resources are elevated by the proper implementation of best practices. This includes its people, processes and technology all working together seamlessly.
As a framework, ITIL is meant to provide guidance without codified standards. There are no “musts” in ITIL only “shoulds” and possibilities. Managers can choose to implement the practices that apply most readily to their business model while skipping other ITIL practices that aren’t applicable at the moment.
There were seven books that made up the catalog of ITIL best practices, condensed from 30 books originally. They included:
- Service Support
- Service Delivery
- Planning to Implement Service Management
- ICT Infrastructure Management
- Applications Management
- Security Management
- The Business Perspective
In 2007, these were re-evaluated and condensed further into the five ITIL books widely used today. Let’s look at each one in turn.
ITIL Service Strategy
ITIL Service Strategy principles help organizations adapt to a market-driven approach to service management. Delivery and support of services and products are encouraged using five tenets, as follows:
- Service portfolio management
- Financial management for IT services
- Demand management
- Business relationship management
- Strategy management for IT services
ITIL Service Design
The RACI matrix offers key insight on ITIL Service Design. RACI stands for responsible, accountable, consulted and informed. Using this matrix, organizations are encouraged to come up with prioritized business objectives for which IT products and services can be deployed.
The tenets of ITIL Service Design are:
- Design Coordination
- Service catalogue management
- Service-level management
- Capacity management
- IT service continuity management
- Security management
- Supplier management
ITIL Service Transition
This refers to a project development facet that exists outside of day-to-day IT functions. It focuses on the following tenets:
- Transition planning and support
- Change management
- Service asset and configuration management
- Release and deployment management
- Service validation and testing
- Change evaluation
- Knowledge management
ITIL Service Operation
ITIL Service Operation is all about best practices. It offers insight on how to deliver on end-user expectations while being cost conscious and uncovering issues. ITIL service operation can be separated into two main groups: Processes and Functions.
Functions include:
- Technical management
- Service desk
- Application management
- IT Ops management
Processes include:
- Fulfilment
- Problem management
- Incident management
- Event management
- Access management
ITIL Continual Service Improvement
This is ITIL’s philosophy for improving service beyond transition. It has seven major tenets:
- Identify strategy for improvement
- Define what you will measure
- Gather data
- Process data
- Analyze information
- Present / Use the information
- Implement improvement